Installation Guide for Windows
This guide supplies step-by-step instructions for installing the required tools for the course.
Before You Begin
First, create accounts for the following services if you have not already:
Additionally, accept the invite for your section on Slack. You will receive the link to your class-specific channel during orientation.
Microsoft Excel
We will be using a free trial version of Microsoft Office 365 for the Excel portion of this class.
- Follow the link and install Office 365. You will not be charged anything as long as you cancel before the free trial period ends.
There are also several free alternatives to Microsoft Excel, such as Google Sheets and Apache OpenOffice. You are more than welcome to use one of these, but be aware that we will be using Excel in class and there may be some differences in commands and functionality.
VS Code
-
Go to the setup page on the VS Code website and select Windows as your platform.
-
When the download is complete, run the installer file
VSCodeSetup-version.exe.
Note For a 64-bit machine, VS Code is installed under
C:\Program Files \(x86\)\Microsoft VS Code.
Git and Git Bash
Follow these instructions to set your Git username for every repository on your computer and set your email address for every repository on your computer.
-
Go to the Git Downloads page. Select the download for Windows. It should automatically download the most up to date version.
-
Click Next to progress through the installation until you get to the screen that asks you to choose a default editor for Git. Select Use Visual Studio Code as Git's default editor.

- When you see a prompt like this, select Checkout as-is, commit Unix-style line endings.

- Finally, select Use Windows' default console window.

Any settings not mentioned here can be left in their default mode.
SSH Keys
Generating SSH keys allows developers to interface with certain remote services without having to constantly enter login information. You will set up an SSH key for GitHub.
Without a key, you won’t be able to push your code to GitHub without entering a password each time. And trust us, this would be as irritating as needing a key to open every door in your home.
To complete these steps, you will need to sign up for a GitHub account if you haven't already.
Use the following walkthrough video alongside the steps outlined below to add GitHub SSH keys:
-
Open Bash.
-
To make sure you don’t already have a set of keys on your computer, type the following in your Bash window. (Note: Copying and pasting will not work!)
ls –al ~/.ssh
- If no keys pop up, move on to Step 3.
- If keys do pop up, check that none of them are listed under `id_rsa`, like in this image:
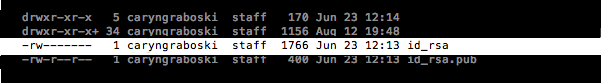
- If you find a key with a matching name, you can either overwrite it by following the next steps, or you can use the same key referenced in Step 8. If you decide not to overwrite it, you will need to remember the password tied to your key.
- Enter the following command along with your email to generate your keys.
ssh-keygen –t rsa –b 4096 –C "YOURGITHUBEMAIL@PLACEHOLDER.NET"
- When prompted to enter a file to save the key, press Enter, and then enter a passphrase for your key. Note: You shouldn’t see any characters appear in the window while typing the password. When you’re finished, your window should look like this:

-
Link your key to your machine using a tool called the ssh-agent. Run the following command in Bash to test whether the ssh-agent is running on your machine:
eval "$(ssh-agent –s)".Your Bash window should look like the following:

-
Run the following command:
ssh-add ~/.ssh/id_rsa -
When prompted, enter the passphrase associated with the key.
Note If you’ve forgotten this key, go back to Step 3.
-
To add the key to GitHub, copy the key to your clipboard by entering the following command:
clip < ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub- You shouldn’t see any kind of message when you run this command. If you do, make sure you entered it correctly.
Note Do not copy anything else to your clipboard until all steps are completed. Otherwise, you’ll need to enter the copy command again.
-
Go to GitHub's SSH key settings. Click New SSH key.
-
When the form pops up, enter a name for your computer in the Title input. In the Key input, paste the SSH key you copied in Step 8.
-
To add GitHub to your computer’s list of acceptable SSH hosts, type the following command in your Bash window:
ssh –T git@github.com.- You should see an RSA fingerprint in your window. Enter yes only if it matches the one highlighted in the image below:

Install Anaconda for Python
We just have one more tool to download before you are ready to go. Use the following link to install Anaconda for Python:
You're Done!
That's all for the installations. Your machine has everything it needs to hit the ground running on the first day of class!